| Welcome, Guest |
You have to register before you can post on our site.
|
| Online Users |
There are currently 21 online users.
» 0 Member(s) | 21 Guest(s)
|
| Latest Threads |
Automatisierte FTP Sicher...
Forum: Deutsch
Last Post: savas
02-02-2020, 02:59 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 5,584
|
Sicherungssoftware, die F...
Forum: Deutsch
Last Post: savas
02-02-2020, 02:28 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 3,734
|
Wie ist eine Windows 10 H...
Forum: Deutsch
Last Post: savas
02-02-2020, 02:15 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 3,432
|
Top 6 Best Backup Softwar...
Forum: Lists
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 06:54 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 4,378
|
VM Cloud Backup for Virtu...
Forum: How-to Guides
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 06:29 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 4,634
|
Is Windows 10 Hyper-V bac...
Forum: Q & A
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 06:06 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 4,789
|
Backup software that supp...
Forum: Q & A
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 06:01 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 3,803
|
Windows 10 backup to ftp ...
Forum: Q & A
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 05:48 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 4,274
|
How to assign drive lette...
Forum: Q & A
Last Post: savas
01-27-2020, 05:36 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 3,823
|
Map Drive Over Internet W...
Forum: How-to Guides
Last Post: savas
10-03-2018, 03:22 PM
» Replies: 0
» Views: 5,123
|
|
|
| The shadow copies of volume were deleted... consider reducing the IO load |
|
Posted by: savas - 08-12-2018, 12:41 PM - Forum: Q & A
- No Replies
|
 |
Let's break down the Windows error message:
"The shadow copies of volume C: were deleted because the shadow copy storage could not grow in time. Consider reducing the IO load on the system or choose a shadow copy storage volume that is not being shadow copied." 
Compressed error messages like above need to be read multiple times with high concentration and lot's of coffee... 
When a backup is done using VSS, a shadow of the partition (example C is created. is created.
The backup proceeds reading from the shadow, not the from actual C: drive.
What is a shadow? A 'fake' and consistent view of the hard drive from the past. The hard drive is being backed up live, that means other applications are constantly changing files. But we want a consistent view, not a live view.
Remember what happens when you take a photo with very long shutter speed at night and there is motion? It will end up looking blurred.
What you want is a snapshot, so fast, that there is no motion and the pic is sharp. With backups we want a 100% exact representation of what the C: drive looked like at a certain time.
And this representation must be kept alive for as long as the backup takes. That representation of the drive's exact past content is a 'volume shadow' provided by VSS.
Now VSS has to keep 'faking' this past view of the drive's contents, and it's hard work when there are lots of applications writing to the hard drive, changing content. VSS has to buffer all the changed sectors, in order to preserve the past content of the changed sectors.
Hence, the more write activity occurs, the more buffering VSS has to do. VSS uses a hidden file to buffer these changes to sectors. hence, it can potentially run out of space if that buffer file gets too big (as a result of too many sectors being changed on disk during backup).
But the problem here is not space.
The error says " storage could not grow in time" and that means TIME is the issue. When these buffering activities take too long, because they are too many, caused by "too much" writing to disk, VSS would potentially have to choke the entire system in order to catch up in order to keep the shadow alive. Because of a hard fixed timeout inside VSS, it then decides to abandon ship and delete the shadow. Naturally the backup then fails because the device it reads from suddenly disappears.
So to recap, this is a situation where "too much" writing occurs to disk, more than the HW can handle in reasonable time. "Reasonable" is simply a timeout inside VSS that can't be changed.
What causes "too much" writing to disk? The message actually tells you what to look into: "Consider reducing the IO load on the system". This means there are services/applications that are hammering the disk with block changes. Remember every changed block has to be 'rescued' by VSS in a buffer file, so each written sector will end up hitting the disk twice.
Now factor in that this is a mechanical disk. So there are sector seek times of 10-50 ms, potentially for most affected sectors.
Factor in, the drive may be heavily fragmented. Fragmentation requires heads to move around much more, and this increases seek time.
Factor in, a potentially unfortunate setup: someone took a desktop drive and loaded it up with 10 VMs that are likely disk-heavy. A desktop drive is not a suitable medium for VM activity, which is very heavy. 10 VMs is the load of 10 entire servers! Putting that on a cheap desktop drive for production purposes, is, well let's call it 'uninformed'.... 
This brings us to another important guideline:
When you design and build servers (or order them custom-built if you're allergic to electronics), you absolutely must isolate the load to separate RAID arrays (or at least disks).
You could build a huge RAID array for your VMs or DBs with say 64TB space, all in one chunk. Problem: VSS right now won't work with more than 16TB (which is a problem as the biggest HDD is already 14TB today).
Second problem, even if it did support 64TB, VSS works at the partition level.
If you put 64TB all in one partition, then VSS has to buffer all changes of the entire 64TB partition for the duration of a backup, even if you just want to back up a small 100GB VM....
You see that would also be unfortunate....but you will find it in too many companies...
At the very least, you could split the 64TB into smaller partitions, still using the same RAID array underneath, that's OK. Then strategically place VMs in a way so that the write load of all VMs combined is distributed, not most inside one partition.
Even better for performance and backups: use completely separate RAID arrays. 
|

|
|
| Backup Hyper-V while running: Backup VM, guest machines while online |
|
Posted by: savas - 06-22-2018, 08:36 AM - Forum: How-to Guides
- No Replies
|
 |
You can back up Hyper-V while running and while guest virtual machines are running without interrupting them.
To back up Hyper-V with running virtual machines, use BackupChain and create a backup task of Hyper-V Backup type. There you can select the VM from a list and specify the target folder. You can back up VMs while running to a local drive, network drive, and also directly to FTP sites.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/M1zYXTwDJ-o" frameborder="0" allow="autoplay; encrypted-media" allowfullscreen></iframe>
BackupChain contains more features to fine-tune your Hyper-V VM backups, for example, granular backup. Granular backup for Hyper-V can open VHD files and other formats while the VM is running and back up individual files and folders from inside the virtual machine.
|

|
|
| How to Speed up Slow Backups and Improve Backup Speed |
|
Posted by: savas - 06-22-2018, 07:47 AM - Forum: How-to Guides
- No Replies
|
 |

It’s a general knee jerk reaction to blame your backup solution for being slow; however, slow backup performance is often caused by many other factors. Whether you use Windows Server Backup, Veeam, BackupChain, or Acronis, when used in the same underlying infrastructure the bottleneck may be identical; hence, you’ll want to identify the real bottleneck in your setup.
You can speed up your backup process considerably and identify slow performers by using this checklist below:
Check for orphaned VSS snapshots and delete them
On some systems the hardware is so slow that people get impatient and terminate the backup process before it finishes.
This should never be done. Backup services should never be terminated by hand, unless it’s an emergency or last-resort situation.
Because if you do kill the process, no clean up occurs and the server gradually fills up with garbage shadows, a.k.a. orphaned shadows.
VSS Snaphots are somewhat tricky to understand. Basically each snapshot tracks the previous state of the drive, while new changes are written directly to disk. As you can imagine, if you have many snapshots the system will be very slow when reading as well as writing, since it needs to manage each snapshot separately all the time.
Some users deploy VSS snapshots to enable file version recovery through Windows Explorer. That’s fine if there is just one shadow, but if you have many, you basically burn expensive, ongoing server performance for something that a backup solution can do much better in a short period of time. Consider using backups instead at regular nightly intervals.
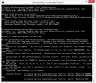
To check for and clean up VSS snapshots, open the command prompt as administrator and use vssadmin.exe list shadows as shown below:

On Windows Server 2008 and later, there’s a nice UI tool available for this as well, in case you have command prompt phobia, it’s called VSSUIRUN.EXE.
As you see above, the system is clean. If it wasn’t there would be a range of shadows in the system. Note that during backups you will see the actual shadow listed there, so don’t delete it while the backup is active.
Increase Shadow Storage Area
VSS is error prone when it runs out of space. Use vssadmin (or VSSUIRUN.EXE if available) to increase the VSS area limits for all drives.
The command
vssadmin list shadowstorage
will report on the current allocation limits.
Use ‘vssadmin resize shadowstorage’ and set all drives to ‘unbounded’ or a very large portion of the disk’s space.
Note that this is only a limit, VSS won’t actually use it unless it has to.
Free Disk Space
Another common reason for slow backups and actually slow overall system performance has to do with how NTFS operates.
You should aim for 20% free disk space to keep the system running optimally. Less than that and write access will slow down considerably. In addition, disk fragmentation will be highly likely resulting from a near-full disk in the future, which in turn will slow down read accesses as well.
Turn off System Restore
Turn off System Restore (on desktop versions of Windows) or scheduled VSS snapshot creation (on Windows Servers). System Restore is supposed to help you return your PC to a bootable state, for example, when you install drivers and it blue-screens.
However, as noted above, VSS slows down the system too much to make this a feasible option, especially when System Restore runs on a schedule and creates many shadows over time. Consider using system backups instead. The backup will run once and consume a lot of resources when doing so, but once finished the system returns to full capacity for your other applications. This type of backup strategy is advantageous especially for lower powered systems.
Disk Fragmentation
Disk fragmentation is highly recommended for source drives as well as backup disks.
|

|
|
| Backup, Clone, or Copy? Disk Cloning vs. Disk Imaging vs. Copying |
|
Posted by: savas - 06-22-2018, 07:38 AM - Forum: Q & A
- No Replies
|
 |
There are several disk backup concepts that are related and the terms are sometimes used interchangeably; however, there are major differences in how and why these backups are done.
What is Disk Backup, a.k.a. Disk Imaging?
When you back up a disk, you create a disk image file that contains the contents of the physical disk you are backing up. The backup software reads the disk and creates a disk image file with the disk contents in it. The advantage here is that you have a file that is likely going to be smaller than the actual disk and you can copy it elsewhere later and archive it. Disadvantage is usually, but not always, that most software uses proprietary formats for these disk image files, but some backup solutions also offer open standard formats for disk images, such as BackupChain.
Another disadvantage here is that the entire disk needs to be scanned in order to create a disk image or an incremental disk image of it.
What is Disk Copying?
Disk copying usually means you want to copy an entire disk to another physical disk at the sector level. Note that would create an exact clone and the problem with that idea is that operating systems do not like to have disk clones connected simultaneously because that would confuse the system. Each disk must have a unique ID; otherwise, the operating system cannot work with it. Ergo, exact disk clones can only be created by a disk duplication system or by keeping the disks always offline, i.e. unmounted.
What is Live Disk Cloning?
Live disk cloning is a technology that allows you to clone a disk to another physical disk while the operating system and all applications are in use. The disk clone can be mounted side-by-side with the original disk, because it has its own unique ID, and is hence because of that not an exact clone; however, the cloned disk can be used to boot Windows and is otherwise identical to the original.
When to Choose Which?
A good Windows Server 2016 backup solution should offer all of the above options, including file-level backup. Disk cloning should be considered for servers where downtime is an issue. Disk image backups, on the other hand, need time to be restored to a new disk. When you have a clone ready to go, all that needs to be done is a change in the BIOS boot settings and the system is ready to reboot.
For data disks, a disk clone is immediately accessible and can also serve as a time-delayed mirror, because it isn't mirroring the data instantaneously like a RAID mirror array. Disk cloning requires that the target disk is always available, online, and physically connected to the server (exception iSCSI and other attached remote storage), whereas disk images can be stored anywhere on other disks or arrays or NAS servers, for example.
And finally a copied disk has the advantage that its contents are immediately available in a way that is native to the operating system, unlike disk images that either require a restore or specialized (usually proprietary) software to access files and folders.
|

|
|
| Pros and Cons of Disk Cloning and Disk Imaging |
|
Posted by: savas - 06-22-2018, 07:10 AM - Forum: Pros and Cons
- No Replies
|
 |
I would recommend using disk cloning and imaging backup software:
1. if you need to support a large number of PC users who are likely to run into problems with their PCs. Such as viruses, configuration problems.
2. If you are a home user who wants to protect the system from a hard drive crash or other damage
Advantages of image backups:
1. The entire system is stored in a single file which you can copy to an external hard drive
2. System can quickly be restored on the same computer after replacing a hard drive.
Disadvantages of image backups and disk cloning:
1. The new hard drive is likely to be bigger than the old one. You end up with some extra space left over and will need another tool to enlarge the partition or create new ones. In Windows 7 and later you can do that via the disk management console.
2. Strictly speaking, you need a new software license on your new PC if you want to restore a backup from your crashed PC
3. Images are usually stored in a proprietary format. You can only access your files using that program (which you need to buy in case you don’t have it anymore or in case you want to restore the system elsewhere)
4. Microsoft and other software vendors lock software to the hardware of your PC. If you restore the image on the same PC you will be able to get it to work fine. However, on a new PC the hardware codes and IDs are different and you need to re-activate Windows and all the other software
5. If you restore the image on a new PC, it’s likely that you will get blue screens or worse, intermittent crashes. So either the system won’t boot, or it will be unstable. This is because the drivers don’t match your new PC’s hardware. Most of the time I tried to restore an image to a new system, it didn’t work and couldn’t be made to work either.
6. Image backups take a long time to complete, even in incremental/differential backup mode. If your system is big you’re better off just backing up specific folders using file backup software.
7. Image backup software isn’t that smart yet. It’s all or nothing. Either the image can be created/restored in full or you end up with nothing. For example, if your external drive ends up being too small you won’t know until you have the backup run for hours and then it will stop saying ‘drive is full’. It will complain about the drive being full and leave you with no backup at all. At least with a file backup, you would have most of your files in case of an emergency.
8. On a new computer it is generally recommended, if not required, to reinstall everything from scratch. At least then you know you have a clean system running smoothly!
However if you want to protect against simple hard drive failure, it’s definitely the way to go because it will save you time restoring the system. Whether you use image backups or file backups, I found external hard drives very convenient and fast.
|

|
|
|